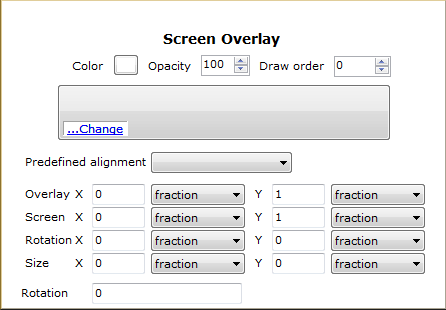
This element draws an image overlay fixed to the screen. Sample
use for screen overlays are compasses, logos, and heads-up displays. Screen
overlay sizing is determined by the Size X, Y. Positioning of
the overlay is handled by mapping a point in the image specified by
Overlay X, Y to a point on the screen specified by
Screen X, Y. Then the image is rotated by
Rotation degrees about a point relative to the screen specified
by Rotation X, Y.
Color:
Opacity:
Draw
order: Icon
(...Change): Predefined alignment:
Opens a
Color dialog. The color white is equivalant to removing
the color, that is, the icon will not have its color
altered.
A ratio indicating how opaque the icon is.
The ratio is between 0 for transparant and 100 for fully
opaque.
This element defines the stacking order for
the images in overlapping overlays. Overlays with higher draw order values
are drawn on top of overlays with lower draw order values.
Open the extended images pick list dialog
to define the image associated with the Overlay. This location can be
either on a local file system or on a web server. If this element is
omitted or contains no path, a rectangle is drawn using the color and size
defined by the ground or screen overlay.
Helps you quickly set the screen overlay to a predefined
position ie: top-left, middle,
bottom-right,...
Specifies a point on (or outside of) the overlay image that is mapped to the screen coordinate Screen X, Y. It requires x and y values, and the units for those values.
The x and y values can be specified in three different ways: as pixels, as fractions of the image fraction, or as inset pixels insetPixels, which is an offset in pixels from the upper right corner of the image. The x and y positions can be specified in different ways—for example, x can be in pixels and y can be a fraction. The origin of the coordinate system is in the lower left corner of the image.
Specifies a point relative to the screen origin that the overlay image is mapped to. The x and y values can be specified in three different ways: as pixels, as fractions of the screen, or, as insetPixels, which is an offset in pixels from the upper right corner of the screen. The x and y positions can be specified in different ways—for example, x can be in pixels and y can be a fraction. The origin of the coordinate system is in the lower left corner of the screen.
For example, Screen X =. 5, y = .5, x unit = fraction, y unit = fraction indicates a point in the middle of the screen.